SEC595: Applied Data Science and AI/Machine Learning for Cybersecurity Professionals


Experience SANS training through course previews.
Learn MoreLet us help.
Contact usBecome a member for instant access to our free resources.
Sign UpWe're here to help.
Contact Us
Apply your credits to renew your certifications
Attend a live, instructor-led class from a location near you or virtually from anywhere
Course material is geared for cyber security professionals with hands-on experience
Apply what you learn with hands-on exercises and labs
Learn to defend every layer of your GenAI stack including applications, models, and MLOps in modern cloud environments.
Ahmed is the best cybersecurity instructor I have seen. He has the ability to demystify complex subjects and make them look easy.
SEC545 gives you the practical skills to design, secure, and defend GenAI applications by understanding real risks, applying proven security controls across RAG, agents, and MLOps workflows, and developing threat models and defenses that strengthen your organization's AI systems.
Prefer to learn OnDemand and start today? The SEC545S: (3 Day) course is still available OnDemand for immediate access.
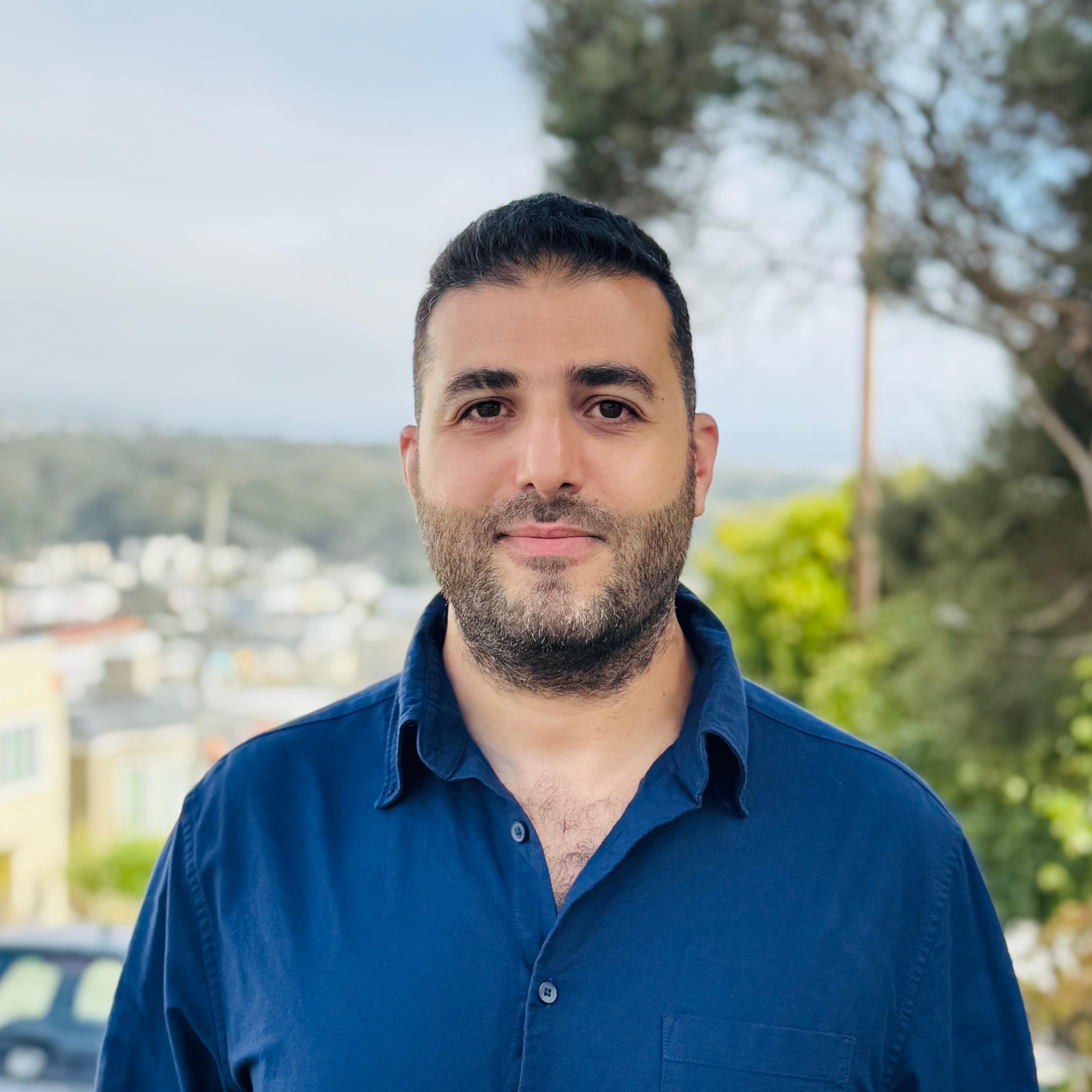


Ahmed is the founder of Cyberdojo with 17+ years in cloud, network, and application security. He specializes in GenAI security and has led projects in cloud security, application security, and incident response.
Read more about Ahmed AbugharbiaExplore the course syllabus below to view the full range of topics covered in SEC545: GenAI and LLM Application Security.
The course starts with GenAI fundamentals, covering key concepts like Large Language Models (LLMs), embeddings, and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Students will explore security risks unique to GenAI, including prompt injection, malicious models, and third-party supply chain vulnerabilities.
Section 2 dives into core components for GenAI apps, like vector databases, LangChain and AI agents. Students also explore deployment zstrategies, comparing cloud and on-premises setups with a focus on the security risks unique to each. The section concludes by introducing agents communication protocols such as MCP.
In Section 3, students continue exploring MCP security before diving into Transformers, the core technology behind LLMs. They examine the foundation of predictive modeling, evaluate secure hosting options for AI applications, and conclude with securing data orchestration pipelines and tools such as Airflow.
Section 4 focuses on MLOps and integrating security across pipelines. It covers model-specific attacks like serialization flaws and backdoors, then explores securing pipelines using controls such as model signing and automated scanning. The section ends with a hands-on AI threat modeling exercise using the MAESTRO framework.
Section 5 covers using AI for threat hunting and incident investigation and response, followed by a Capture the Flag (CTF) exercise. Students apply what they’ve learned to identify and remediate issues within AI infrastructure that includes Kubernetes, Docker Compose, MCP servers, Airflow, SageMaker, AWS Bedrock, and other cloud environments.
Cloud Security Engineers integrate advanced security measures into cloud and cloud-native environments, maximize security automation within DevOps workflows, and proactively mitigate threats to safeguard modern cloud infrastructures.
Explore learning pathA Cloud Security Analyst monitors and analyzes activity across cloud environments, proactively detects and assesses threats, and implements preventive controls and targeted defenses to protect critical business systems and data.
Explore learning pathResponsible for ensuring that security requirements are adequately addressed in all aspects of enterprise architecture, including reference models, segment and solution architectures, and the resulting systems that protect and support organizational mission and business processes.
Explore learning pathResponsible for conducting software and systems engineering and software systems research to develop new capabilities with fully integrated cybersecurity. Conducts comprehensive technology research to evaluate potential vulnerabilities in cyberspace systems.
Explore learning pathResponsible for planning, implementing, and operating network services and systems, including hardware and virtual environments.
Explore learning pathResponsible for analyzing the security of new or existing computer applications, software, or specialized utility programs and delivering actionable results.
Explore learning pathResponsible for developing and maintaining business, systems, and information processes to support enterprise mission needs. Develops technology rules and requirements that describe baseline and target architectures.
Explore learning pathResponsible for the secure design, development, and testing of systems and the evaluation of system security throughout the systems development life cycle.
Explore learning pathEnroll your team as a group or arrange a private session for your organization. We’ll help you choose the format that fits your goals.

Get feedback from the world’s best cybersecurity experts and instructors
Choose how you want to learn - online, on demand, or at our live in-person training events

Get access to our range of industry-leading courses and resources