SEC595: Applied Data Science and AI/Machine Learning for Cybersecurity Professionals


Experience SANS training through course previews.
Learn MoreLet us help.
Contact usBecome a member for instant access to our free resources.
Sign UpWe're here to help.
Contact UsDue to the notoriety SCATTERED SPIDER and The Com have attracted as prolific cybercriminal threats, law enforcement has been tracking them closely.

In this blog, the authors of SANS FOR589: Cybercrime Intelligence highlight how it was possible to identify, track, profile, and defend against a prolific cybercriminal threat group known as SCATTERED SPIDER, which is part of a broader community of cybercriminals dubbed The Com, which is short for The Community. This includes exploring the cybercrime underground to uncover the same services, tools, infrastructure, and communities that SCATTERED SPIDER participates in.
The emergence and notoriety that SCATTERED SPIDER generated is exemplary of the type of cybercriminal activity FOR589 focuses on. This blog highlights key aspects of how FOR589 will teach students to generate actionable intelligence tracking emerging threats through monitoring cybercriminal activities.
In May 2024, at the cybercrime-focused Sleuthcon conference, the FBI recently warned that there is a community of young mostly English-speaking cybercriminals known as The Com that is responsible for multiple high-profile breaches as well as SIM swapping fraud. It is made up of approximately 1,000 individuals, according to the FBI. Cybersecurity podcasts such as Darknet Diaries and Click Here have also interviewed participants of The Com that provided details about how The Com works.
SCATTERED SPIDER is the most used moniker, coined by CrowdStrike, for the cybercriminal threat group that evolved out of The Com and developed a common set of intrusion techniques observed across multiple high-profile breaches. Will Thomas, the co-author of FOR589, also spoke about this cybercrime group at BSides Cheltenham in June 2023. Other cybercrime groups such as LAPSUS$ are another example of adversaries evolving out of The Com.
SCATTERED SPIDER is known by various other names to different cybersecurity vendors who report on threat groups. This includes UNC3944 (Mandiant), Octo Tempest (Microsoft), 0ktapus (Group-IB), Muddled Libra (PAN Unit 42), and Scatter Swine (Okta). It is also worth noting that what makes tracking and understanding this cybercrime group trickier, is that each cybersecurity vendor may disagree on how these adversaries overlap with each other through indicators of compromise (IOCs) or tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
This confusion, caused by the various vendors using alternative threat group names, highlights the importance and need to track individuals and communities separately through cybercrime intelligence. Simply put, SCATTERED SPIDER does not fit neatly into the current paradigm perpetrated by cybersecurity vendors who prefer to cluster all adversaries neatly like advanced persistence threat (APT) groups only through the lens of intrusion analysis.
Due to the notoriety SCATTERED SPIDER and The Com have attracted as prolific cybercriminal threats, law enforcement has been tracking them closely. There have, so far, been two arrests by US and European law enforcement of individuals reportedly part of this high-profile cybercrime ring known as The Com. In January 2024, US authorities charged a 19-year-old from Florida and in June 2024 a UK citizen was arrested in Spain.
Some of the most well-known victims and targets of this common set of TTPs originating from The Com include big name brands such as HubSpot, Twilio, DoorDash, Okta, Cloudflare, and Activision in 2022. Followed by MailChimp, RiotGames, Reddit, Coinbase, Clorox, MGM, and Caesars in 2023. MGM also disclosed through their US Security Exchange Commission (SEC) filing that the overall cost from the disruption to their operations by the ransomware attack was $100 million USD.
Note that directly attributing intrusions to The Com or SCATTERED SPIDER is difficult unless the victim confirms it themselves. The TTPs deployed against these victims, however, closely align with the capabilities outlined by the various cybersecurity vendors and in joint cybersecurity advisories by government agencies.
The reason it is so hard to defend against the TTPs of The Com is that they use a combination of social engineering methods to gain initial access, and once inside their target environment, they employ various methods to successfully evade modern enterprise security tools. Their common intrusion patterns are not necessarily advanced, but are highly effective, which makes them a significant threat for most large companies.
This includes being able to bypass security tools for host-based defenses, like endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems as well as identity and access management (IAM) tools like single sign-on (SSO). Their knowledge of enterprise Windows environments, multiple cloud tenants, and virtualized infrastructure also makes them difficult to evict from victim networks. Their experience exploiting these enterprise security systems also potentially indicates they have worked with them legitimately in the past.
The common capabilities from threat reports describing those leveraged by members of The Com can be extracted into TTP categories in a table, as shown below.
Tactic | Technique | Threat Report(s) |
Initial Access | SIM Swapping | |
Initial Access | SMS Phishing | |
Initial Access | Spearphishing Voice | |
Defense Evasion | Bring-Your-Own-Vulnerable-Driver (BYOVD) | |
Defense Evasion | Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools | |
Defense Evasion | UEFI Bootkit | |
Privilege Escalation | Exploit CrowdStrike Real-Time-Response (RTR) Console | |
Privilege Escalation | Steal credentials from Password Managers | |
Persistence | Create Virtual Machines | |
Lateral Movement | Exploit the Azure Admin Console | |
Collection | Source Code Repositories | |
Collection | Business SaaS Repositories | |
Exfiltration | Exfiltrate to AWS or GCP cloud storage | |
Command-and-Control | Residential Proxy Services | |
Impact | Deploy ALPHV/BlackCat Ransomware |
It was not realized until mid-2023 that some members of The Com (the SCATTERED SPIDER sub-group) had likely joined forces with the Russian-speaking ransomware gang known as ALPHV/BlackCat. Through the collection of cybercrime intelligence related to intrusions and TTPs attributed to The Com, several technical, behavioral, and temporal overlaps were discovered.
In February 2023, Reddit disclosed publicly that they suffered a data breach and that the root cause was a phishing campaign that targeted Reddit employees using a website that cloned the behavior of Reddit’s intranet gateway, in an attempt to steal credentials and two-factor authentication (2FA) tokens. The TTPs described by Reddit were very similar to the SMS phishing campaigns launched by 0ktapus that spoofed the Okta intranet gateways of many high-profile companies. In June 2023, Reddit was listed as a victim on the ALPHV/BlackCat Tor data leak site (DLS), which was the first indicator that SCATTERED SPIDER was an ALPHV/BlackCat affiliate.
A warning by the Canadian Center for Cyber Security (CCCS) in July 2023 shared the TTPs of a ALPHV/BlackCat affiliate against Canadian companies. This included the use of SMS phishing for SSO access, spearphishing voice calls, multi-factor authentication (MFA) push notification fatigue attacks, and the delivery of RMM tools. Plus, many of the same TTPs described by Coinbase in February 2023 were also present in the CCCS advisory. These reports act as further evidence that these English-speaking cybercriminals had joined forces with a Russian-speaking ransomware group.
To be able to stand a chance against SCATTERED SPIDER and The Com and not end up as their next victim, it is vital for organizations to monitor related activities going on in the cybercriminal underground. This includes identifying examples of where these adversaries can leverage services, tools, access, and resources to launch their intrusions.
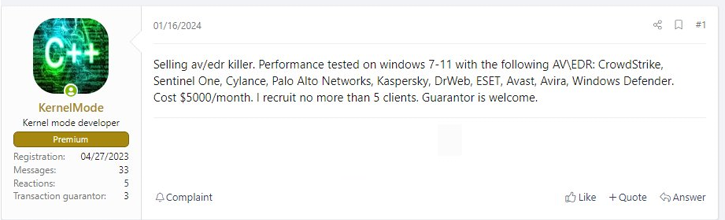
One of the most well-known TTPs used by SCATTERED SPIDER is the BYOVD trick and use of malicious signed drivers to terminate the processes of antivirus (AV) and EDR systems. These types of utilities are often put up for sale on Russian-speaking cybercrime forums, such as XSS forum (formerly DaMaGeLaB) or RAMP (see Figure 1). Another one of these EDR-killing tools called ‘Terminator’ was offered by the RAMP member ‘Spyboy’ for $3,000 USD in May 2023.
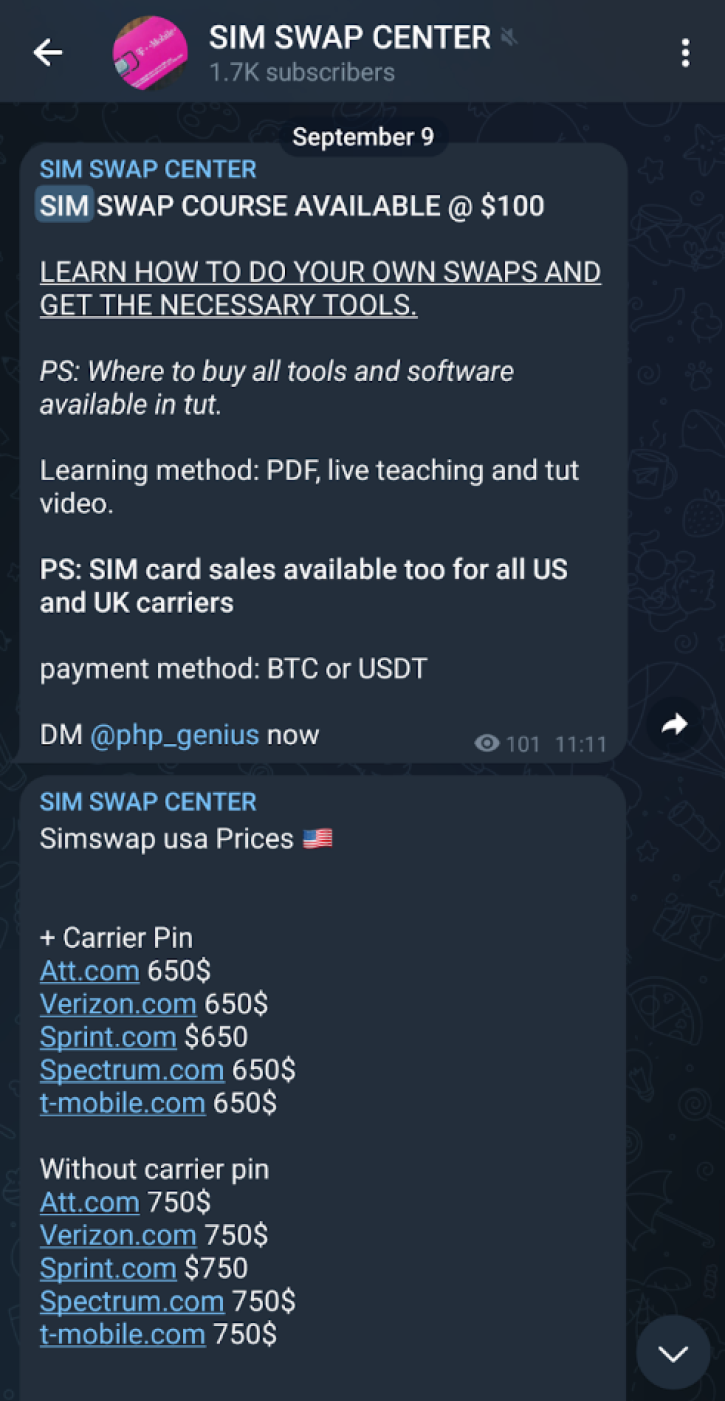
Another TTP commonly associated with threat actors from The Com is SIM swapping. This involves exploiting a mobile carrier’s phone number transfer system to take control of a target’s phone number. This enables a cybercriminal to access SMS messages, such as 2FA codes sent during typical authentication processes. SIM swapping services can be easily found for sale across Telegram channels, with varying levels of legitimacy (see Figure 2).
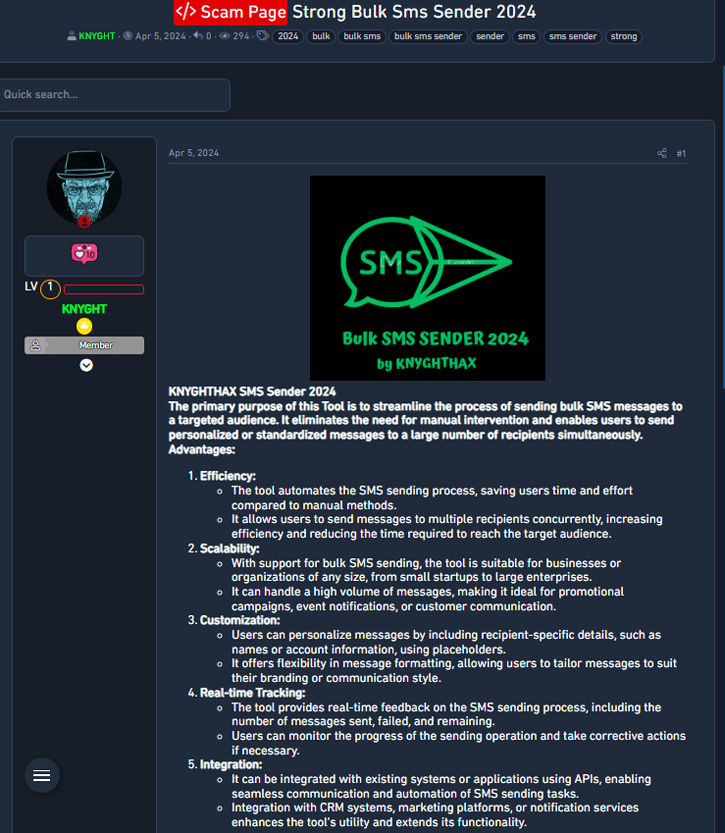
A staple of SCATTERED SPIDER campaigns is the use of SMS bulk message sending services to deliver their phishing links posing as SSO login portals. Interestingly, they use the same services enterprises do for 2FA code delivery, things like parcel delivery updates or marketing, such as Twilio, Telnyx, and Nexmo, among others. These services can be regularly found across the underground from various regions (see Figure 3).
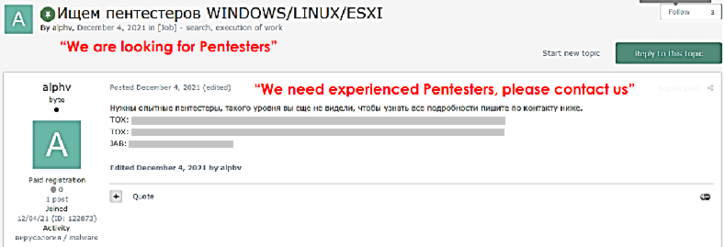
The ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware gang also used to advertise their affiliate program on the Russian-speaking Exploit[.]in cybercrime forum (see Figure 4). The admin ‘alphv’ would post their TOX and Jabber details to the forum and invite other users to apply to join their Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) affiliate program. The members of The Com could easily have joined Exploit forum and reached out to the admin and applied to become an affiliate.
Monitoring the entire cybercrime underground will be a challenge for many organizations, as it may require having a dedicated cybercrime intelligence analyst or vendor who can build personas, infiltrate cybercrime forums and Telegram channels, and maintain that access – all without burning their operational security (OPSEC).
Once an organization is in position to monitor the cybercrime underground, they can gain invaluable insights into the types of services, tools, and access that cybercriminals trade on the underground. Leveraging that knowledge to augment threat-informed defense programs can boost the chances of your organization withstanding the next intrusion attempt.
The outputs from a cybercrime intelligence program as an enterprise can include, custom detection rules, discoveries made during threat hunts, reimplemented processes based on exploitation methods, targeting of partners, subsidiaries, or suppliers; and predictions based on the current trends. All these outputs will contribute toward preventing breaches and can support resource and investment prioritization strategies if leveraged effectively.
The cybercrime underground is an additional dataset and telemetry for organizations to hunt through for their own benefit and look for threats towards their organization, technology stack, and suppliers.
There are various best practices that enterprise security teams can follow to defend against SCATTERED SPIDER and The Com, which are as follows:
In conclusion, defending against sophisticated cybercriminal groups like SCATTERED SPIDER and The Com requires a proactive and comprehensive approach. By understanding their TTPs and continuously monitoring the cybercrime underground, organizations can significantly enhance their cyber defense strategies. SANS FOR589: Cybercrime Intelligence is designed to equip you with the skills and knowledge needed to identify, track, and counter these threats effectively. Don't wait for an attack to occur—take the initiative to safeguard your organization today.
Sign up for a demo or register for FOR589: Cybercrime Intelligence now and become adept at generating actionable intelligence to defend against the most notorious cyber threats.


Will has revolutionized cyber threat intelligence by co-founding Curated Intelligence and exposing ransomware operations like Black Basta. His expertise in infiltrating dark web communities has advanced how we dismantle cybercriminal networks.
Read more about Will Thomas