SEC595: Applied Data Science and AI/Machine Learning for Cybersecurity Professionals


Experience SANS training through course previews.
Learn MoreLet us help.
Contact usBecome a member for instant access to our free resources.
Sign UpWe're here to help.
Contact Us
I have seen the following Windows Prefetch entries in nearly every Windows XP / Vista machine that I have reviewed over the past several years.Their existence always reminds me of the imperfect nature of information gained via individual artifacts.Does this mean that a user ran the Microsoft Defragmenter application on July 16, 2009 at 1:19PM?Or was the defragmenter started automatically by Windows?The defragmenter tool has been used very effectively as an anti-forensic tool since it was first introduced.In cases where data spoliation could be important, it is critical for the examiner to be able to identify any overt actions by a user.Complicating this is that starting with Windows XP, the operating system conducts limited defragmentation approximately every three days. [1] This post seeks to identify forensic artifacts which can help us determine if a user initiated the defrag application.

We will focus on two primary methods a user can invoke the Windows Defragmenter tool:
The GUI defragmenter tool leaves a wealth of artifacts that can distinguish user execution of defrag from system execution.It is commonly accessed from the Start Menu -> Accessories -> System Tools menu.We will query the following artifacts to identify user actions:
The addition of Windows Prefetch in XP has provided investigators with an excellent artifact for identifying applications executed on a system.While it won't give us everything we need in this situation, it is an excellent starting point.Entries are located in the C:\Windows\Prefetch directory and can be parsed using Mark McKinnon's Prefetch Parser or your favorite forensic suite.
When the defragmenter is run using the GUI, only the dfrgntfs.exe entry is updated within the Prefetch directory (with an updated access time stamp and execution count).This immediately reveals that the artifacts shown in Figure 1 were not left by the GUI tool.It may also explain why we often see higher execution counts for dfrgntfs.exe than defrag.exe when parsing the Prefetch entries.As an aside, it is interesting to note that I found differences in how the execution count was updated.When using the GUI, the execution value for dfrgntfs.exe was incremented by one and when using the command line application, the counts were incremented by three.
Since the GUI version of the defragmenter is essentially a Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-in, an entry for MMC.exe is also created in the Prefetch folder.It is important to note that MMC.exe can be present in the Prefetch due to the use of other snap-ins (such as viewing the event logs).Its proximity to the dfrgntfs.exe entry is one clue, but Prefetch files can also show what was loaded by the application, and further investigation reveals that dfrgres.dll and dfrgui.dll are both loaded by MMC.exe whenever it facilitates the defragmenter snap-in.

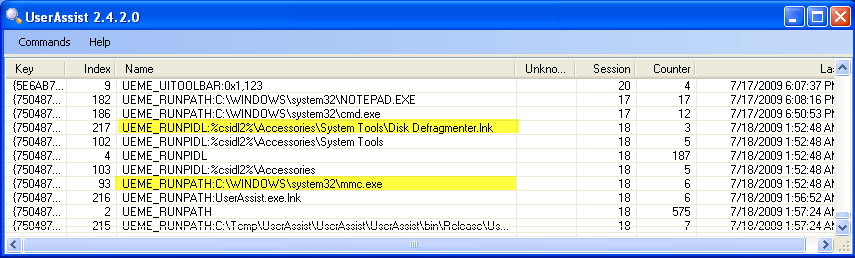
Prefetch can indicate that the GUI application was run, but it gives no information regarding user attribution.Luckily we have an artifact available in the NTUSER.dat hive file that does both.The UserAssist registry key, HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\Currentversion\Explorer\UserAssist\{GUID}\Count, stores information on applications run per user.This is a terrific artifact for proving user activity and can be easily viewed using UserAssist.exe written by Didier Stevens.Evidence of manual execution can be found within this registry key when the defragmenter is accessed via the GUI interface.You should be looking for entries for "Disk Defragmenter.lnk" and "mmc.exe".The "Last" time indicates when the application was last run by the user.One unfortunate limitation of this artifact is that applications run from the command line are not recorded.
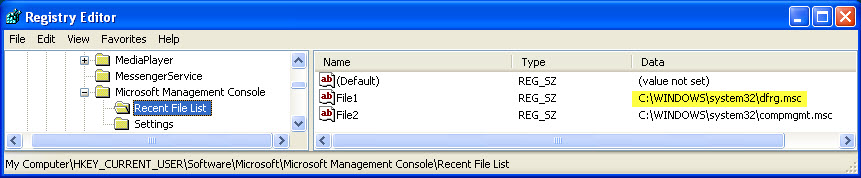
Since we know that the MMC is utilized by the defragmenter GUI, there is an additional registry artifact dedicated to recording MMC usage.Looking at HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Microsoft Management Console\Recent File List, we should see an entry for dfrg.msc, which is the Microsoft Common Console file for the defragmenter snap-in.If this is the last value recorded, the key last write time will indicate when the defragmenter was last run.Additionally, note that this registry key is under HKey_Current_User (NTUSER.dat hive), giving us another artifact for proving user attribution.
Finally, we can tie everything together neatly by doing a timestamp analysis.The access timestamps for the following files indicate when these files were last run.Any mismatch with the times indicated in the Prefetch and UserAssist artifacts can tell us if there was any additional defrag activity after the GUI was run:
In contrast to our investigation of artifacts generated by the GUI interface, command line use of the defrag tool gives us much fewer artifacts to work with.We will be required to focus on:
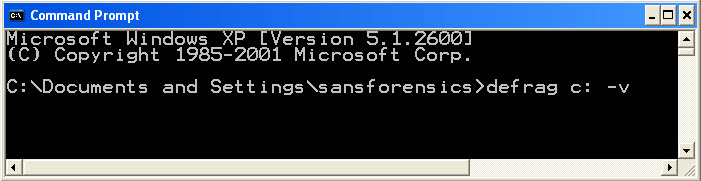
Unlike the artifacts for the GUI defragmenter, the Prefetch artifacts left by command line execution of defrag.exe are the same as those left by the Windows automated process.Upon command line execution both defrag.exe and dfrgntfs.exe are created in the Prefetch directory.Further, their last access times are updated to the time the application was run.This tells us when the defrag tool was last run, but does not allow us to differentiate between system defrags and user generated activity.Therefore we will need to turn to timeline analysis.
With very limited artifacts, old fashioned timeline analysis will likely be our best bet to identify user defrag activity.This is not a theoretical exercise.We have seen instances of the defrag tool used as an anti-forensics tool in recent intrusion cases.Often this plays out with the intruder installing their payload on the system, deleting it, and then running defrag.exe to prevent the malware from being recovered by incident responders.

In this situation we will often be looking for the opening of a command shell (cmd.exe) near the time that defrag.exe was run.This is a key differentiator since Windows does not require an interactive command shell when kicking off automated processes.Figure 6 shows how this might look in the Prefetch directory.In addition to just Prefetch entries, other timeline entries like created and deleted files can provide further context.Admittedly, this evidence is very temporal and presumes that collection occurs as close a possible to the time the intrusion occurred.
The layout.ini file is located in the C:\Windows\Prefetch directory and is used by the Prefetch process to more efficiently place system and frequently used applications during the limited defrag sequence.It is not used during a standard manual defragmentation.Therefore it can be a good indicator for distinguishing between user and system actions.In the example shown in Figure 7, the modification time of the layout.ini coincides with the defrag applications and indicates that they were run by the operating system (not the user).
A Note Regarding Event Logs
In Windows XP, there is no native capability to record defragmenter usage in the event logs.[2]Thus we will not be able to leverage this source of information as we could for other actions like task scheduler usage.
We stand our best chance of tying defragmenter execution to a user account if it was conducted via the GUI interface.Many of our most valuable Windows artifacts are not updated when an application is run from the command line.However, we will often be able to turn to old-fashioned timeline analysis to assist in these circumstances.
It should be noted that there are plenty of legitimate reasons for running the defragmenter tool.Other contemporaneous actions need to be reviewed to assess a user's true intent.
The Vista operating system changes many of the artifacts covered in this post.Part 2 will cover performing this analysis on a Vista system.
Chad Tilbury, GCFA, has spent over ten years conducting computer crime investigations ranging from hacking to espionage to multi-million dollar fraud cases. He teaches FOR408 Windows Forensics and FOR508 Advanced Computer Forensic Analysis and Incident Response for the SANS Institute. Find him on Twitter @chadtilbury or at http://ForensicMethods.com.


As a Special Agent with the Air Force Office of Special Investigations, Chad served on the national computer intrusion team and helped expand counter-espionage techniques. At SANS, Chad is a senior instructor and co-author for FOR500 and FOR508.
Read more about Chad Tilbury